Ethylnorepinephrine
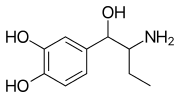
Ethylnorepinephrine (Etanor, Bronkephrine, Butanefrine) is a sympathomimetic and bronchodilator related to norepinephrine.[1][2][3] It activates both α and β adrenergic receptors.[4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | β,3,4-trihydroxy-N-ethyl-2-phenylethylamine |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H15NO3 |
| Molar mass | 197.234 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
See also
References
- David J. Triggle (1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC. ISBN 0-412-46630-9.
- KORNEL L (1958). "A case of calcified ventricular aneurysm with progressive heart block; observations on the effect of ethylnorepinephrine". Cardiologia. 32 (2): 101–9. doi:10.1159/000165806. PMID 13500349.
- CHRISTENSEN JM, VALASEK FE, TAINTER ML (June 1958). "Ethylnorepinephrine; a unique bronchodilator". American Practitioner and Digest of Treatment. 9 (6): 916–21. PMID 13533786.
- Turner, Robert A. (1965). "12. Sympatholytic Agents. VI. The Two Kinds of Receptors". Screening Methods in Pharmacology. 111 Fifth Avenue, New York, New York 10003: Academic Press Inc. p. 150. ISBN 1483255913.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link)
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.