Normetanephrine
Normetanephrine is a metabolite of norepinephrine created by action of catechol-O-methyl transferase on norepinephrine. It is excreted in the urine and found in certain tissues. It is a marker for catecholamine-secreting tumors such as pheochromocytoma.

Norepinephrine degradation. Normetanephrine is shown at top left. Enzymes are shown in boxes.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
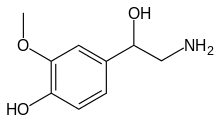
| IUPAC name
4-(2-amino-1-hydroxy-ethyl)- 2-methoxy-phenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Normetanephrine |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H13NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 183.204 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Figure 11-4 in: Flower, R.; Rang, H. P.; Dale, M. M.; Ritter, J. M. (2007). Rang & Dale's Pharmacology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-443-06911-6.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.