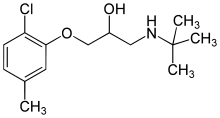
Bupranolol
Bupranolol is a non-selective beta blocker without intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA), but with strong membrane stabilizing activity. Its potency is similar to propranolol.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral, topical (eye drops) |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | < 10% |
| Protein binding | 76% |
| Metabolism | First pass elimination > 90% |
| Elimination half-life | 2-4 hours (plasma) |
| Excretion | > 88% renal (as carboxybupranolol) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H22ClNO2 |
| Molar mass | 271.79 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Uses and dosage
Like other beta blockers, oral bupranolol can be used to treat hypertension and tachycardia. The initial dose is 50 mg two times a day. It can be increased to 100 mg four times a day. Bupranolol eye drops (0.05%-0.5%) are used against glaucoma.
Pharmacology
Bupranolol is quickly and completely absorbed from the gut. Over 90% undergo first-pass metabolism. Bupranolol has a plasma half life of about two to four hours, with levels never reaching 1 µg/l in therapeutic doses. The main metabolite is carboxybupranolol, 4-chloro-3-[3-(1,1-dimethylethylamino)-2-hydroxy-propyloxy]benzoic acid – that is, the methyl group at the benzene ring is oxidized to a carboxyl group –, of which 88% are eliminated renally within 24 hours.
Adverse effects, contraindications, interactions
Adverse effects, contraindications and interactions are similar to other beta blockers.
References
Further reading
- Dinnendahl V, Fricke U (2007). Arzneistoff-Profile (in German). Vol. 2 (21 ed.). Eschborn, Germany: Govi Pharmazeutischer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-7741-9846-3.