Cloranolol
Cloranolol (Tobanum) is a beta blocker.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
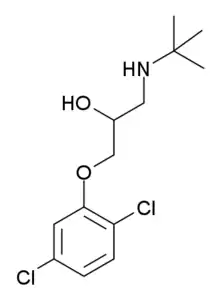
| IUPAC name
(RS)-1-(tert-butylamino)-3-(2,5-dichlorophenoxy)propan-2-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H19Cl2NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 292.20 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| C07AA27 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Synthesis
β-Adrenergic blocker. Prepn:[2]
References
- Kulcsár-Gergely J. (July 1989). "Action of beta-adrenoceptor blockers on liver function of rats". Arzneimittelforschung. 39: 782–5. PMID 2571334.
- G. Richter, DE 2213044, "Racemisches und optisch aktives 1-(2,5-Dichlorphenoxy)-3-tert.butylamino-2-propanol und ihre Salze, sowie ihre Verwendung und Verfahren zu deren Herstellung derselben [Racemic and optically active 1-(2,5-dichlorophenoxy)-3-tertbutylamino-2-propanols and their salts, as well as their use and process for their preparation]", published 1972-09-28, assigned to Richter Gedeon Vegyeszeti Gyar R.T..
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.