Bornaprolol
Bornaprolol is a beta-adrenergic antagonist.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
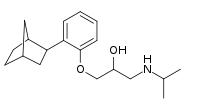
| IUPAC name
1-[2-(3-Bicyclo[2.2.1]heptanyl)phenoxy]-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H29NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 303.446 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Cheymol, G; Jaillon, P; Lecoq, B; Lecoq, V; Cheymol, A; Krumenacker, M (1987). "Cardiovascular beta-adrenergic blocking effects of bornaprolol in humans: Relation to dose and plasma concentration". Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 9 (6): 694–8. doi:10.1097/00005344-198706000-00009. PMID 2442536. S2CID 38782602.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.