2-Fluoromethamphetamine
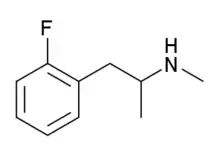
2-Fluoromethamphetamine (2-FMA) is a stimulant drug of the amphetamine family which has been used as a designer drug .[1][2] It is purported to possess little recreational value because it lacks the euphoric effects typical of other amphetamines. 2-FMA is commonly compared to lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse) in its duration, potency and efficacy as a study or productivity aid.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H14FN |
| Molar mass | 167.227 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Chemistry
2-Fluoromethamphetamine is fluorinated analogue of methamphetamine, and is a regioisomer of 3-FMA and 4-FMA
Legal status
China
As of October 2015, 2-FMA is a controlled substance in China.[3]
Germany
As of December 13, 2014, 2-FMA is a controlled substance in Germany.[4] It is controlled under Anlage I BtMG (Narcotics Act, Schedule I).[5] Substances controlled under Anlage I BtMG are illegal to manufacture, possess, import, export, buy, sell, procure or dispense it without a license. Violations of the law are punishable by a fine or imprisonment for up to five years. [6]
Ukraine
As of July 2019, 2-FMA is a controlled substance in Ukraine (considered a narcotic). [7]
See also
References
- Rösner P, Quednow B, Girreser U, Junge T (March 2005). "Isomeric fluoro-methoxy-phenylalkylamines: a new series of controlled-substance analogues (designer drugs)". Forensic Science International. 148 (2–3): 143–56. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2004.05.003. PMID 15639609.
- Camilleri A, Johnston MR, Brennan M, Davis S, Caldicott DG (April 2010). "Chemical analysis of four capsules containing the controlled substance analogues 4-methylmethcathinone, 2-fluoromethamphetamine, alpha-phthalimidopropiophenone and N-ethylcathinone". Forensic Science International. 197 (1–3): 59–66. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2009.12.048. PMID 20074881.
- "关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知" (in Chinese). China Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2015. Archived from the original on 1 October 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- Bundesgesetzblatt. "Achtundzwanzigste Verordnung zur Änderung betäubungsmittelrechtlicher Vorschriften - Vom 5. Dezember 2014" (in German). Bundesanzeiger-Verlags-GmbH. Retrieved 6 April 2022.
- Bundesministerium der Justiz. "Gesetz über den Verkehr mit Betäubungsmitteln (Betäubungsmittelgesetz - BtMG) Anlage I (zu § 1 Abs. 1) (nicht verkehrsfähige Betäubungsmittel)" (in German). Retrieved 6 April 2022.
- Bundesministerium der Justiz. "Gesetz über den Verkehr mit Betäubungsmitteln (Betäubungsmittelgesetz - BtMG) § 29 Straftaten" (in German). Retrieved 6 April 2022.
- "Про внесення змін до Закону України "Про обіг в Україні наркотичних засобів, психотропних речовин, їх аналогів і прекурсорів"" (in Ukrainian). Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine. 23 July 2019. Archived from the original on 6 September 2021. Retrieved 6 September 2021.