Cloniprazepam
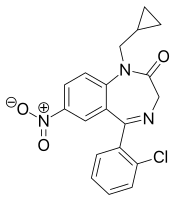
Cloniprazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative and a prodrug of clonazepam, 7-aminoclonazepam, and other metabolites.[1][2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 1-Cyclopropylmethylclonazepam, Kloniprazepam, 2-Chloro-7'-nitroprazepam |
| Drug class | Benzodiazepines |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H16ClN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 369.81 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |

Metabolic pathway of cloniprazepam
Some of the minor metabolites include 3-hydroxyclonazepam and 6-hydroxyclonazepam, 3-hydroxycloniprazepam and ketocloniprazepam with ketone group formed where 3-hydroxy group was.[1]
It is a designer drug and an NPS (short for "new psychoactive substance").[1] At the end of 2017, cloniprazepam was an uncontrolled substance in most of the countries.
See also
References
- Moosmann B, Bisel P, Franz F, Huppertz LM, Auwärter V (November 2016). "Characterization and in vitro phase I microsomal metabolism of designer benzodiazepines - an update comprising adinazolam, cloniprazepam, fonazepam, 3-hydroxyphenazepam, metizolam and nitrazolam". Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 51 (11): 1080–1089. Bibcode:2016JMSp...51.1080M. doi:10.1002/jms.3840. PMID 27535017.
- Mortelé O, Vervliet P, Gys C, Degreef M, Cuykx M, Maudens K, et al. (May 2018). "In vitro Phase I and Phase II metabolism of the new designer benzodiazepine cloniprazepam using liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry". Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 153: 158–167. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2018.02.032. hdl:10067/1496330151162165141. PMID 29494888. S2CID 3946404.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.