Buthalital
Buthalital sodium (INN; Bayinal, Baytinal, Thialbutal, Transithal, Ulbreval), or buthalitone sodium (BAN), is a barbiturate derivative which was under development as a short-acting anesthetic.[1][2] However, development was discontinued, perhaps due to its extremely rapid elimination rate,[3] and buthalital sodium was never marketed.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
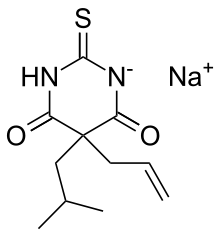
| Formula | C11H15N2NaO2S |
| Molar mass | 262.30 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
See also
References
- Macdonald F (1997). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. p. 338. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- Martin JR, Godel T, Hunkeler W, Jenck F, Moreau JL, Sleight AJ, Widmer U (2000). "Psychopharmacological Agents". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.1619250313011820.a01. ISBN 0471238961.
- Wollweber H (2000). "Anesthetics, General". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_289.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.