Transverse acetabular ligament
The transverse acetabular ligament (transverse ligament or Tunstall’s ligament) is a portion of the acetabular labrum, though differing from it in having no cartilage cells among its fibers.
| Transverse acetabular ligament | |
|---|---|
 Left hip-joint, opened by removing the floor of the acetabulum from within the pelvis. (Trans. ligament labeled at center.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ligamentum transversum acetabuli |
| TA98 | A03.6.07.009 |
| TA2 | 1881 |
| FMA | 43518 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
It consists of strong, flattened fibers, which cross the acetabular notch, and convert it into a foramen through which the nutrient vessels enter the joint. It is an intra-articular structure of the hip.[1]
Function
The transverse acetabular ligament prevents inferior displacement of head of femur.
Additional Images
 Hip joint. Lateral view. Transverse acetabular ligament
Hip joint. Lateral view. Transverse acetabular ligament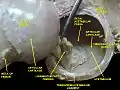 Hip joint. Lateral view. Transverse acetabular ligament
Hip joint. Lateral view. Transverse acetabular ligament
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 336 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 336 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Lee, Soon Hyuck; Jang, Woo Young; Choi, Gi Won; Lee, Young Keun; Jung, Hae Woon (April 2018). "Is the Transverse Acetabular Ligament Hypertrophied and Hindering Reduction in Developmental Dysplasia of Hip?". Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic & Related Surgery. 34 (4): 1219–1226. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2017.10.024. ISSN 0749-8063. PMID 29287953.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.