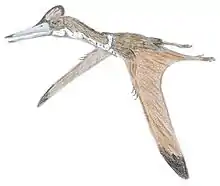
Thanatosdrakon
Thanatosdrakon (IPA: [θænətɒsdrɑːkɒn]) (meaning "dragon of death") is a genus of quetzalcoatline pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Upper Coniacian–Lower Santonian) Plottier Formation of the Neuquén Basin in western Argentina. The type and only species is T. amaru, known from two specimens consisting of several well-preserved axial and appendicular bones including material previously undescribed in giant azhdarchids (e.g. complete notarium, dorsosacral vertebrae and caudal vertebra). Thanatosdrakon is one of the oldest known members of the Quetzalcoatlinae.[1]
| Thanatosdrakon Temporal range: Upper Coniacian – Lower Santonian, ~ | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Order: | †Pterosauria |
| Suborder: | †Pterodactyloidea |
| Family: | †Azhdarchidae |
| Subfamily: | †Quetzalcoatlinae |
| Genus: | †Thanatosdrakon Ortiz David et al., 2022 |
| Species: | †T. amaru |
| Binomial name | |
| †Thanatosdrakon amaru Ortiz David et al., 2022 | |
Description
Thanatosdrakon is known from two specimens: the holotype, UNCUYO-LD 307, a partial postcranial skeleton, and the paratype, UNCUYO-LD 350, a complete left humerus. The holotype specimen has a wingspan of approximately 7 metres (23 ft), suggesting a wingspan of approximately 9 metres (30 ft) for the paratype, making Thanatosdrakon the largest known pterosaur from South America.[1]
Classification
Ortiz David et al., (2022) recovered Thanatosdrakon in the Quetzalcoatlinae subfamily of Azhdarchidae, as a sister taxon to Quetzalcoatlus in a clade with Cryodrakon in a phylogenetic analysis. Their results are shown below:[1]
| Quetzalcoatlinae |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Palaeoecology
Thanatosdrakon is known from the upper-most levels of the Plottier Formation, which represents a floodplain with ephemeral rivers and consists of mudstone, siltstone, claystone and sandstone, suggesting it lived in a continental environment created by the low-gradient wandering rivers that laid down alluvial deposits across the formation.[1]
Thanatosdrakon was contemporaneous with an indeterminate abelisaurid,[2] basal coelurosaurian, unenlagiine, aeolosaurin, saltasaurid, and ornithopod,[3] as well as the lithostrotian titanosaurs Antarctosaurus giganteus,[4] Notocolossus,[5] and Petrobrasaurus.[6][3] Non-dinosaurian taxa from the formation include freshwater bivalves, an indeterminate crocodyliforme and mesoeucrocodylian,[3] the chelid turtles Linderochelys[7] and Rionegrochelys,[8] and at least one indeterminate mammal. Ichnotaxa consist of the burrow ichnogenus Scoyenia sp., and insect ichnogenus Taenidium sp.[3]
References
- Ortiz David, Leonardo D.; González Riga, Bernardo J.; Kellner, Alexander W. A. (12 April 2022). "Thanatosdrakon amaru, gen. ET SP. NOV., a giant azhdarchid pterosaur from the upper Cretaceous of Argentina". Cretaceous Research. 135. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2022.105228. Retrieved 12 April 2022.
- Hendrickx, Christophe; Tschopp, Emanuel; Ezcurra, Martín d. (2020-04-01). "Taxonomic identification of isolated theropod teeth: The case of the shed tooth crown associated with Aerosteon (Theropoda: Megaraptora) and the dentition of Abelisauridae". Cretaceous Research. 108: 104312. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2019.104312. ISSN 0195-6671.
- Plottier Formation at Fossilworks.org
- Antarctosaurus giganteus type locality at Fossilworks.org
- Notocolossus gonzalezparejasi type locality at Fossilworks.org
- Petrobrasaurus puestohernandezi type at Fossilworks.org
- Linderochelys rinconensis type locality at Fossilworks.org
- Rionegrochelys caldieroi type locality at Fossilworks.org