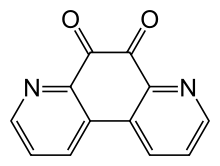
Phanquinone
Phanquinone is an organic compound. It is a yellowish solid derived by oxidation of 4,7-phenanthroline.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.378 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H6N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 210.192 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
It has been investigated as both antiprotozoal agent and for its bactericidal activity .[1]
References
- Mett H, Gyr K, Zak O, Vosbeck K (July 1984). "Duodeno-pancreatic secretions enhance bactericidal activity of antimicrobial drugs". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 26 (1): 35–8. doi:10.1128/aac.26.1.35. PMC 179912. PMID 6236746.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.