Glucotropaeolin
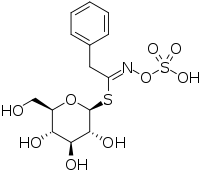
Glucotropaeolin (benzylglucosinolate) is a glucosinolate found in cruciferous vegetables, particularly garden cress.[1] Upon enzymatic activity, it is transformed into benzyl isothiocyanate (BITC). Isothiocyanates are being studied for their toxicity to cancer, which is more generally sensitive to toxins than healthy cells.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-S-[(1E)-2-Phenyl-N-(sulfooxy)ethanimidoyl]-1-thio-beta-D-glucopyranose | |
| Other names
Benzylglucosinolate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 61369 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H19NO9S2 | |
| Molar mass | 409.42 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Refs
- "Isothiocyanates". Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.