Chanoclavine
Chanoclavine, also known as chanoclavin-l is a tri-cyclic ergot alkaloid (ergoline) isolate of certain fungi. It is mainly produced by members of the genus claviceps.[1] Long used in traditional Chinese medicine, it was found in 1987 mouse studies to stimulate dopamine D2 receptors in the brain.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
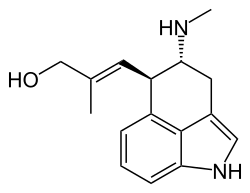
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E)-2-Methyl-3-[(4R,5R)-4-(methylamino)-1,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[cd]indol-5-yl]prop-2-en-1-ol | |
| Other names
chanoclavin-l | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H20N2O | |
| Molar mass | 256.34 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Lorenz, N; Haarmann, T; Pazoutová, S; Jung, M; Tudzynski, P (2009). "The ergot alkaloid gene cluster: Functional analyses and evolutionary aspects". Phytochemistry. 70 (15–16): 1822–32. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.05.023. PMID 19695648.
- Watanabe, H; Somei, M; Sekihara, S; Nakagawa, K; Yamada, F (1987). "Dopamine receptor stimulating effects of chanoclavine analogues, tricyclic ergot alkaloids, in the brain". Japanese Journal of Pharmacology. 45 (4): 501–6. doi:10.1254/jjp.45.501. PMID 3127619.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.