Quercinol
Quercinol (a chromene derivative), isolated from the mushroom Daedalea quercina, has in vitro anti-inflammatory activity, and inhibits the enzymes cyclooxygenase 2, xanthine oxidase, and horseradish peroxidase.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
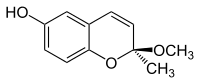
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S)-2-Methoxy-2-methyl-2H-1-benzopyran-6-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H12O3 | |
| Molar mass | 192.214 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Gebhardt P, Dornberger K, Gollmick FA, Gräfe U, Härtl A, Görls H, Schlegel B, Hertweck C (May 2007). "Quercinol, an anti-inflammatory chromene from the wood-rotting fungus Daedalea quercina (Oak Mazegill)". Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17 (9): 2558–60. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.02.008. PMID 17346963.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.