Prodiamine
Prodiamine is a preemergent herbicide of the dinitroaniline class. Prodiamine is used with crops such as soybeans, alfalfa, cotton, and ornamental crops. Prodiamine inhibits the formation of microtubules.[2]
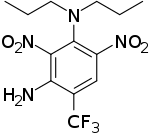 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,6-Dinitro-N1,N1-dipropyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzene-1,3-diamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.914 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H17F3N4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 350.298 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 124–125 °C (255–257 °F; 397–398 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H332, H410 | |
| P261, P271, P273, P304+P312, P304+P340, P312, P391, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Prodiamine was developed by Sandoz AG and marketed beginning in 1987.[3]
Prodiamine can be obtained from 2,4-dichlorobenzotrifluoride by reaction with nitric acid in the presence of sulfuric acid, dipropylamine, and ammonia.[4]
References
- Endeshaw, Molla M; Li, Catherine; Leon, Jessica de; Yao, Ni; Latibeaudiere, Kirk; Premalatha, Kokku; Morrissette, Naomi; Werbovetz, Karl A (2010). "Synthesis and evaluation of oryzalin analogs against Toxoplasma gondii". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 20 (17): 5179. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.07.003. PMC 2922421. PMID 20675138.
- "Herbicide Mode-Of-Action Summary". Purdue University.
- Entry on Prodiamin. at: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, retrieved 8 June 2020.
- Thomas A. Unger (1996). Pesticide Synthesis Handbook. p. 877. ISBN 978-0-8155-1401-5.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.