Oroidin
Oroidin is a bromopyrrole alkaloid, originally isolated from sponges in the genus Agelas. Oroidin possesses moderate antimalarial activity.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
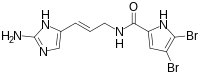
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-[(2E)-3-(2-Amino-1H-imidazol-5-yl)prop-2-en-1-yl]-4,5-dibromo-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H11Br2N5O | |
| Molar mass | 389.051 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Gademann, K.; Kobylinska, J. (2009). "Antimalarial natural products of marine and freshwater origin". Chemical Record. 9 (3): 187–198. doi:10.1002/tcr.200900001. PMID 19424997.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.