Hydrogen-powered aircraft
A hydrogen-powered aircraft is an aeroplane that uses hydrogen fuel as a power source. Hydrogen can either be burned in a jet engine or another kind of internal combustion engine, or can be used to power a fuel cell to generate electricity to power a propeller. Unlike most aircraft, which store fuel in the wings, hydrogen-powered aircraft are usually designed with the hydrogen fuel tanks inside the fuselage.
.jpg.webp)
According to research at the Pennsylvania State University in 2006, large commercial hydrogen aircraft could have been built by 2020 but "will probably not enter service until closer to 2040."[1] In the nearer term, interest has grown in using fuel cell aircraft as personal air vehicles.
Hydrogen properties
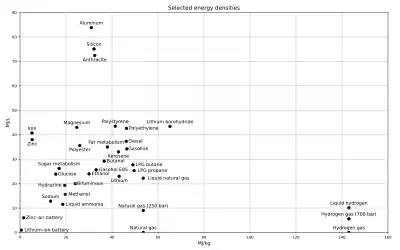
Hydrogen has a specific energy (120 MJ/kg)[2] that is 2.8 times higher than traditional jet fuel (43 MJ/kg).[3] Cryogenic liquid hydrogen has a 4.1 times lower energy density (8.5 MJ/L compared to 35 MJ/L), but needs to be cooled at 20 K (−253 °C) and kept in insulated but low-pressure tanks; while gaseous hydrogen has a lower energy density, needs high pressure tanks reaching up to 700 bar, often in carbon fiber, but can be kept at usual temperatures.
If hydrogen is available in quantity from low-carbon power such as wind or nuclear, its use in aircraft will produce fewer greenhouse gases (water vapor and a small amount of nitrogen oxide) than current aircraft. Currently very little hydrogen is produced using low-carbon energy sources, and there are several serious obstacles to the use of hydrogen in aircraft and other vehicles.[4] Due to the way it is produced, and the relative inefficiencies of its production given current technology, hydrogen is more expensive than fossil fuels.
Liquid hydrogen is one of the best coolants used in engineering, and precooled jet engines have been proposed to use this property for cooling the intake air of hypersonic aircraft, or even for cooling the aircraft's skin itself, particularly for scramjet-powered aircraft.[5]
Design considerations
Liquid hydrogen is 4.1 times less energy dense than kerosene based jet-fuel; and storing the liquid hydrogen needs a pressurised tank with a minimal surface for minimal thermal insulation weight, leading towards cylindrical tanks in the fuselage rather than wet wings in conventional aircraft. This leads to a longer, wider fuselage; adding more skin friction drag and wave drag due to the extra wetted area; extra tank weight; and weight and balance variations during flight.
As hydrogen specific energy is 2.8 times higher than jet-fuel, an hydrogen aircraft would need 2.8 times less fuel weight for the same range, ignoring the repercussion of added volume and tank weight. As airliners have a fuel fraction of the MTOW between 26% for medium-haul to 45% for long-haul, maximum fuel weight could be reduced to 9% to 16% of the MTOW, but this would be the case only for the unusual maximum fuel case of the payload-range tradeoff. The efficiency of a hydrogen-fueled aircraft is a trade-off of the larger wetted area, lower fuel weight and added tank weight, varying with the aircraft size.
Hydrogen aircraft using a fuel cell design are zero emission in operation, whereas aircraft using hydrogen as a fuel for a jet engine or an internal combustion engine are zero emission for CO2 but not for NOx: the burning of Hydrogen in air leads to the production of NOx. I.e. the H2 + O ->H20 reaction in a nitrogen-rich environment also causes the production of NOx.[6]
History
In February 1957, a Martin B-57B of the NACA flew on hydrogen for 20 min for one of its two Wright J65 engines rather than jet fuel.[7] On 15 April 1988, the Tu-155 first flew as the first hydrogen-powered experimental aircraft,[8] an adapted Tu-154 airliner.
The European Union's research project in cooperation with Airbus and 34 other partner companies dubbed CRYOPLANE assessed the technical feasibility, safety, environmental compatibility and economic viability of using liquid hydrogen as an aviation fuel. This was concluded in 2002 (with the final report published in 2003).[9]
Boeing converted a 2-seat Diamond DA20 to run on a fuel cell.[11] It first flew on April 3, 2008.[12] The Antares DLR-H2 is a hydrogen-powered aeroplane from Lange Aviation and the German aerospace center.[13] In July 2010, Boeing unveiled its hydrogen powered Phantom Eye UAV, that uses two converted Ford Motor Company piston engines.[14]
In 2010, the Rapid 200FC concluded six flight tests fueled by gaseous hydrogen. The aircraft and the electric and energy system was developed within the European Union's ENFICA-FC project coordinated by the Politecnico di Torino.[15] Hydrogen gas is stored at 350 bar, feeding a 20 kW (27 hp) fuel cell powering a 40 kW (54 hp) electric motor along a 20 kW (27 hp) lithium polymer battery pack.
On January 11, 2011, an AeroVironment Global Observer unmanned aircraft completed its first flight powered by a hydrogen-fueled propulsion system.[16]

Developed by Germany’s DLR Institute of Engineering Thermodynamics, the DLR HY4 four-seater was powered by a hydrogen fuel cell, its first flight took place on September 29, 2016.[17] It has the possibility to store 9 kg (20 lb) of hydrogen, 4x11 kW fuel cells and 2x10 kWh batteries.[18]
In September 2020, Airbus presented three ZEROe hydrogen-fuelled concepts aiming for commercial service by 2035:[19] a 100-passenger turboprop, a 200-passenger turbofan, and a futuristic design based around a blended wing body.[20] The aircraft are powered by gas turbines rather than fuel cells.[21]
In March 2021, Cranfield Aerospace Solutions announced the Project Fresson switched from batteries to hydrogen for the nine-passenger Britten-Norman Islander retrofit for a September 2022 demonstration.[22] Project Fresson is supported by the Aerospace Technology Institute in partnership with the UK Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy and Innovate UK.
As of 2021, ZeroAvia is actively developing aircraft with a fuel cell powertrain "capable of carrying up to 20 passengers about 350 nautical miles".[20]
In December 2021, the UK Aerospace Technology Institute (ATI) presented its FlyZero study of cryogenic liquid hydrogen used in gas turbines for a 279 passengers design with 5,250 nmi (9,720 km) of range.[23] ATI is supported by Airbus, Rolls-Royce, GKN, Spirit, General Electric, Reaction Engines, Easyjet, NATS, Belcan, Eaton, Mott MacDonald and the MTC.
In August 2021 the UK Government claimed it was the first to have a Hydrogen Strategy. This report included a suggested strategy for hydrogen powered aircraft along with other transport modes.[24]
Pratt & Whitney wants to associate its geared turbofan architecture with its Hydrogen Steam Injected, Inter‐Cooled Turbine Engine (HySIITE) project, to avoid carbon dioxide emissions, reduce NOx emissions by 80%, and reduce fuel consumption by 35% compared with the current jet-fuel PW1100G, for a service entry by 2035 with a compatible airframe.[25] On 21 February 2022, the US Department of Energy through the OPEN21 scheme run by its Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) awarded P&W $3.8 million for a two-year early stage research, to develop the combustor and the heat exchanger used to recover water vapour in the exhaust stream, injected into the combustor to increase its power, and into the compressor as an intercooler, and into the turbine as a coolant.[25]
In February 2022, Airbus announced a demonstration of a liquid hydrogen-fueled Turbofan, with CFM International modifying the combustor, fuel system and control system of a GE Passport, for a first flight expected within five years, mounted on a fuselage pylon on an A380 prototype.[26]
In March 2022, FlyZero detailed its three concept aircraft:
- the 75-seat FZR-1E regional airliner has six electric propulsors powered by fuel cells, a size comparable to the ATR 72 with a larger fuselage diameter at 3.5 m (11 ft) compared to 2.8 m (9 ft 2 in) to accommodate hydrogen storage, for a 325 kn (601 km/h) cruise and a 800 nmi (1,480 km) range;
- its FZN-1E narrowbody has rear-mounted hydrogen-burning turbofans, a T-tail and nose-mounted canards, a 10 m (33 ft) longer fuselage than the Airbus A320neo becoming up to 1 m (3 ft 3 in) wider at the rear to accommodate two cryogenic fuel tanks, and a larger wingspan requiring folding wing-tips for a 2,400 nmi (4,400 km) range with a 450 kn (830 km/h) cruise;
- the small widebody FZM-1G is comparable to the Boeing 767-200ER, flying 279 passengers over 5,750 nmi (10,650 km), with a 6 m (20 ft) wide fuselage diameter closer to the A350 or 777X, a 52 m (171 ft) wingspan within airport gate limits, underwing engines and tanks in front of the wing.[27]
Proposed aircraft
Historical
- Lockheed CL-400 Suntan, 1950's concept, dropped for the SR-71
- National Aerospace Plane, 1986-1993 concept with a scramjet
- Tupolev Tu-155, 1988 modified Tupolev Tu-154
- AeroVironment Global Observer, 2010-2011 fuel-cell powered drone demonstrator
- Boeing Phantom Eye, 2012-2016 piston engine powered drone demonstrator
Projects
- Project Fresson, a Britten-Norman Islander retrofit
- Reaction Engines Skylon, orbital hydrogen fuelled jet plane
- Reaction Engines A2, antipodal hypersonic jet airliner
- DLR Smartfish, two seat experimental lifting body; with previous Hyfish model
- ZeroAvia HyFlyer (fuel-cell powered Piper PA-46 demonstrator)[28]
See also
References
- Maniaci, David C. "Operational Performance Prediction of a Hydrogen-Fueled Commercial Transport" 2006 symposium paper Archived 2006-09-05 at the Wayback Machine
- College of the Desert, “Module 1, Hydrogen Properties”, Revision 0, December 2001 Hydrogen Properties. Retrieved 2014-06-08.
- IOR Energy. List of common conversion factors (Engineering conversion factors). Retrieved 2008-10-05.
- "Hydrogen aircraft". H2 Vehicles. Archived from the original on 2012-06-18. Retrieved 2016-05-06.
- Segal, Corin (2010). The Scramjet Engine Processes and Characteristics. Cambridge University Press. p. 4. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511627019. ISBN 9780511627019.
- Mike Menzies (23 September 2019). "Hydrogen: The Burning Question". The Chemical Engineer. Institution of Chemical Engineers.
- Guy Norris (October 1, 2020). "Will Contrails Be Hydrogen Fuel's Achilles' Heel?". Aviation Week.
- Dieter Scholz, Hamburg University of Applied Sciences (19 November 2020). "Design of Hydrogen Passenger Aircraft" (PDF).
- Airbus Deutschland "Liquid Hydrogen Fuelled Aircraft - CRYOPLANE Final Technical Report" 2003
- Robertson, David (2008-04-03). "Boeing tests first hydrogen powered plane". The Times. London.
- "Boeing Prepares Fuel Cell Demonstrator Airplane for Ground and Flight Testing" (Press release). Boeing. March 27, 2007.
- "Boeing Flies First Fuel Cell-Powered Airplane" (Press release). Boeing. April 3, 2008.
- "DLR motor glider Antares takes off in Hamburg – powered by a fuel cell" (PDF) (Press release). DLR. 7 July 2009.
- "Boeing Unveils Unmanned Phantom Eye Demonstrator" (Press release). Boeing. July 12, 2010.
- "ENFICA-FC".
- "Global Observer, AeroVironment's Extreme Endurance Unmanned Aircraft System, Achieves Historic First Hydrogen-Powered Flight" (Press release). AeroVironment. Jan 11, 2011.
- "Fuel cell aircraft HY4 makes maiden flight". The Engineer. 30 September 2016.
- "Vil ha kortdistanse flytrafikk over på hydrogen" (in Norwegian). Teknisk Ukeblad. 21 June 2017.
- "Airbus reveals new zero-emission concept aircraft" (Press release). Airbus. 21 September 2020.
- Henderson, Caspar (7 April 2021). "The hydrogen revolution in the skies". bbc.com. BBC. Retrieved 5 August 2021.
- Tidey, Alice (21 September 2020). "Airbus unveils concepts for zero-emission planes powered by hydrogen". euronews.
- "Project Fresson to deliver world's first truly green passenger carrying airline services using hydrogen fuel cell technology" (Press release). Cranfield Aerospace Solutions. 30 March 2021.
- Nathan Harrison (6 Dec 2021). "Zero-carbon emission flights to anywhere in the world possible with just one stop". Aerospace Technology Institute.
- "UK Hydrogen Strategy" (PDF). UK Government. August 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - Dominic Perry (1 March 2022). "P&W sees 2035 service entry potential for revolutionary hydrogen powerplant". Flightglobal.
- "The ZEROe demonstrator has arrived" (Press release). Airbus. 22 February 2022.
- Dominic Perry (11 March 2022). "FlyZero details trio of zero-emission aircraft concepts". FlightGlobal.
- ZeroAvia Conducts UK's First Commercial-Scale Electric Flight, June 23, 2020
External links
- Bjorn Fehrm (February 7, 2020). "Bjorn's Corner: Why e in ePlane shall stand for environment, Part 8". Leeham News.
- Dan Thisdell (9 July 2020). "Forget batteries, is hydrogen the holy grail for carbon-free commercial aviation?". Flightglobal.
