Hoecken linkage
The Hoecken linkage[1] is a four-bar linkage that converts rotational motion to approximate straight-line motion. It is named after Karl Hoecken (1874−1962).[1]
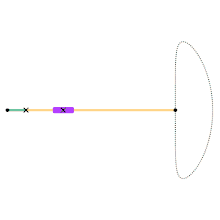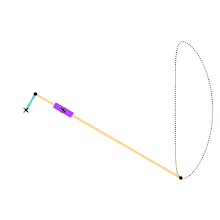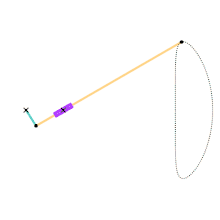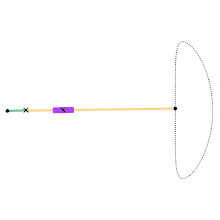
Animation of the Hoecken linkage.
Example Dimensions:
Cyan Link = 1
Yellow Link = 9
Distance between Ground Joints = 2
Example Dimensions:
Cyan Link = 1
Yellow Link = 9
Distance between Ground Joints = 2
The Hoeckens linkage is a cognate linkage of the Chebyshev linkage and Chebyshev's Lambda Mechanism.
The linkage was first published in 1926.[2][3]
A generalization of the Hoecken linkage is Wittgenstein's rod.
See also
- Chebyshev linkage and Chebyshev lambda linkage, linkages that produce a very similar locus without the need of a sliding joint.
- Straight line mechanism
- Four-bar linkage
References
- Ceccarelli, M. (2014). Distinguished Figures in Mechanism and Machine Science: Their Contributions and Legacies. History of mechanism and machine science. Springer London, Limited. ISBN 9789401789479.
- "DMG Lib: Browse, Literature". www.dmg-lib.org.
- Hoecken, Karl. Steigerung der Wirtschaftlichkeit durch zweckmäßige Anwendung der Getriebelehre, Werkstattechnik 1926.
External links
![]() Media related to Hoeckens linkage at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Hoeckens linkage at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.