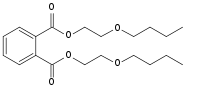
Dibutoxy ethyl phthalate
Dibutoxy ethyl phthalate is a chemical used as a plasticizer in polyvinyl chloride and polyvinyl acetate and used to make adhesives. It has density 0.93 g/ml.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Bis(2-butoxyethyl) benzene-1,2-dicarboxylate | |
| Other names
Bis(2-butoxyethyl) phthalate; Kesscoflex; Kronisol; Palatinol K | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.831 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H30O6 | |
| Molar mass | 366.454 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.93 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H413 | |
| P273, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
8380 mg/kg (oral rat) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Paint Testing Manual. ASTM International. 1972. p. 176.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
